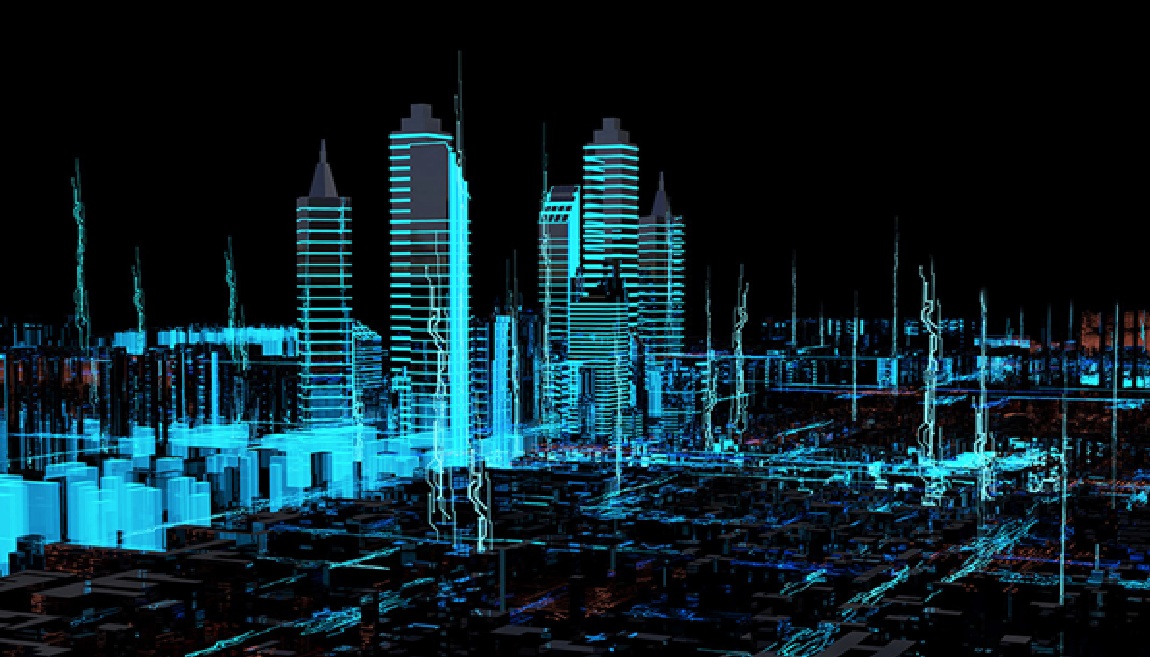
In the 21st century, cities have become the epicenters of human progress, innovation, and opportunity. However, they also stand at the frontline of some of the planet's most urgent challenges—from escalating pollution and traffic congestion to inefficient resource management and growing social inequality. With the United Nations projecting that nearly 68% of the global population will reside in urban areas by 2050, the question is no longer whether cities must evolve, but rather how they can do so to ensure they remain livable, sustainable, and equitable.
A promising solution lies in the concept of digital urbanisation—the integration of digital technologies into the very fabric of urban systems, governance, and everyday life.
Understanding Digital Urbanisation
Digital urbanisation represents more than a mere technological upgrade; it is a paradigm shift in the way cities operate. At its core, digital urbanisation leverages data, connectivity, and advanced information systems to enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and responsiveness of urban environments. This transformation can manifest in various forms—from smart sensors that optimize water supply and waste management, to e-governance platforms that enable citizens to access public services online with greater ease and transparency.
In essence, digital urbanisation is about creating a seamless digital ecosystem in which technology serves as the connective tissue linking citizens, government agencies, infrastructure, and the environment. The goal is not simply to build "smart cities" populated with devices, but to craft intelligent urban systems that improve quality of life while minimizing environmental impact.
The Economic Benefits of Digital Transformation
Digital urbanisation is not only a crucial sustainability strategy but also a powerful economic driver. The adoption of digital technologies in urban areas leads to significant cost reductions, productivity gains, and new avenues for economic growth.
For instance, the implementation of smart grids and intelligent transport systems can optimize energy usage, reduce traffic congestion, and lower operational expenses. Predictive maintenance powered by sensors and data analytics can prevent costly breakdowns in critical infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and pipelines. According to McKinsey Global Institute, smart city technologies can reduce urban infrastructure costs by 10-30% while simultaneously improving outcomes for city residents.
Furthermore, digital urbanisation fosters innovation and entrepreneurship. By embracing data-driven governance, cities attract startups, investors, and businesses focused on sectors like green technology, digital services, and data analytics. The growth of such innovation ecosystems is essential for long-term economic vitality, helping cities stay globally competitive.
A Sustainable Future through Digital Urbanisation
Sustainability is the cornerstone of digital urbanisation. By enhancing the efficiency of resource management and decision-making, digital technologies help reduce waste, carbon emissions, and environmental degradation.
Smart energy systems, for example, balance electricity demand while incorporating renewable sources like solar and wind power. Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical cities—allow urban planners to simulate and assess the environmental impact of proposed infrastructure before construction even begins. Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled monitoring networks provide real-time data on air quality, water usage, and waste collection, enabling cities to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging challenges.
Cities like Singapore and Barcelona offer compelling examples of how digital innovation can drive sustainability. Singapore’s "Virtual Singapore" initiative uses 3D digital modeling to plan urban development with an emphasis on ecological balance. Meanwhile, Barcelona’s smart lighting and waste management systems have not only saved millions of euros but also significantly reduced its carbon footprint.
Promoting Inclusive and Transparent Governance
Digital urbanisation also redefines the governance of cities. With the advent of e-governance platforms, mobile apps, and online dashboards, public services become more accessible, transparent, and participatory.
In India, cities like Surat and Pune, under the Smart Cities Mission, have established Integrated Command and Control Centres (ICCCs) that consolidate the management of traffic, water supply, and emergency response into a single digital platform. These systems not only streamline operations but also foster trust by enabling real-time citizen feedback and monitoring.
However, the true challenge of digital urbanisation lies in ensuring digital inclusion—ensuring that all citizens, regardless of income or education, can benefit from the digital revolution. A truly sustainable smart city must address the digital divide by ensuring affordable internet access, public Wi-Fi, and widespread digital literacy programs.
Challenges and the Road to Progress
Despite its immense potential, digital urbanisation faces several hurdles. Many cities struggle with insufficient financial resources, fragmented governance frameworks, and weak data protection laws. The digital divide remains a critical issue, as unequal access to technology threatens to exacerbate existing social inequalities. Additionally, concerns over data privacy and cybersecurity must be addressed to maintain public trust.
To overcome these challenges, policymakers must adopt inclusive digital strategies, encourage public-private partnerships, and establish robust frameworks for data governance. Investments in digital infrastructure must be complemented by investments in human capital—ensuring that urban administrators, planners, and citizens are equipped with the skills to use data responsibly and effectively.
Conclusion: The Future of Cities
Digital urbanisation presents a transformative opportunity to rethink how cities function. By integrating technology with sustainability and citizen-centered governance, cities can become smarter, more resilient, and economically robust.
The cities that embrace digital innovation today will be the ones that thrive in the future—not merely because they are technologically advanced, but because they are efficient, inclusive, and sustainable.
At its core, digital urbanisation is about creating urban spaces that not only think smarter but also care deeper—about their people, their environment, and their collective future.
0 thoughts on “Digital Urbanisation: The Key to Smart, Sustainable, and Economically Viable Cities”
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
RECENT NEWS
- U.S. shoots down Iranian drone in Arabian Sea: U.S. warship approaches; Iran has already claimed to have developed 1000 drones
- Kremlin responds to Trump's claims on India stopping Russian oil trade: 'No talks held with New Delhi yet'
- UAE announces prayer timings for today: Fajr at 5:37am, Maghrib at sunset
- One million AI satellites to orbit Earth? SpaceX's mind-blowing plan of data centers in outer space explained
- Cricketer Death: Cricketer who took a hat-trick in his debut match in cricket passes away, mourning wave in the cricket world